Mantle Cell Lymphoma on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) is a type of
 MCL, like most
MCL, like most

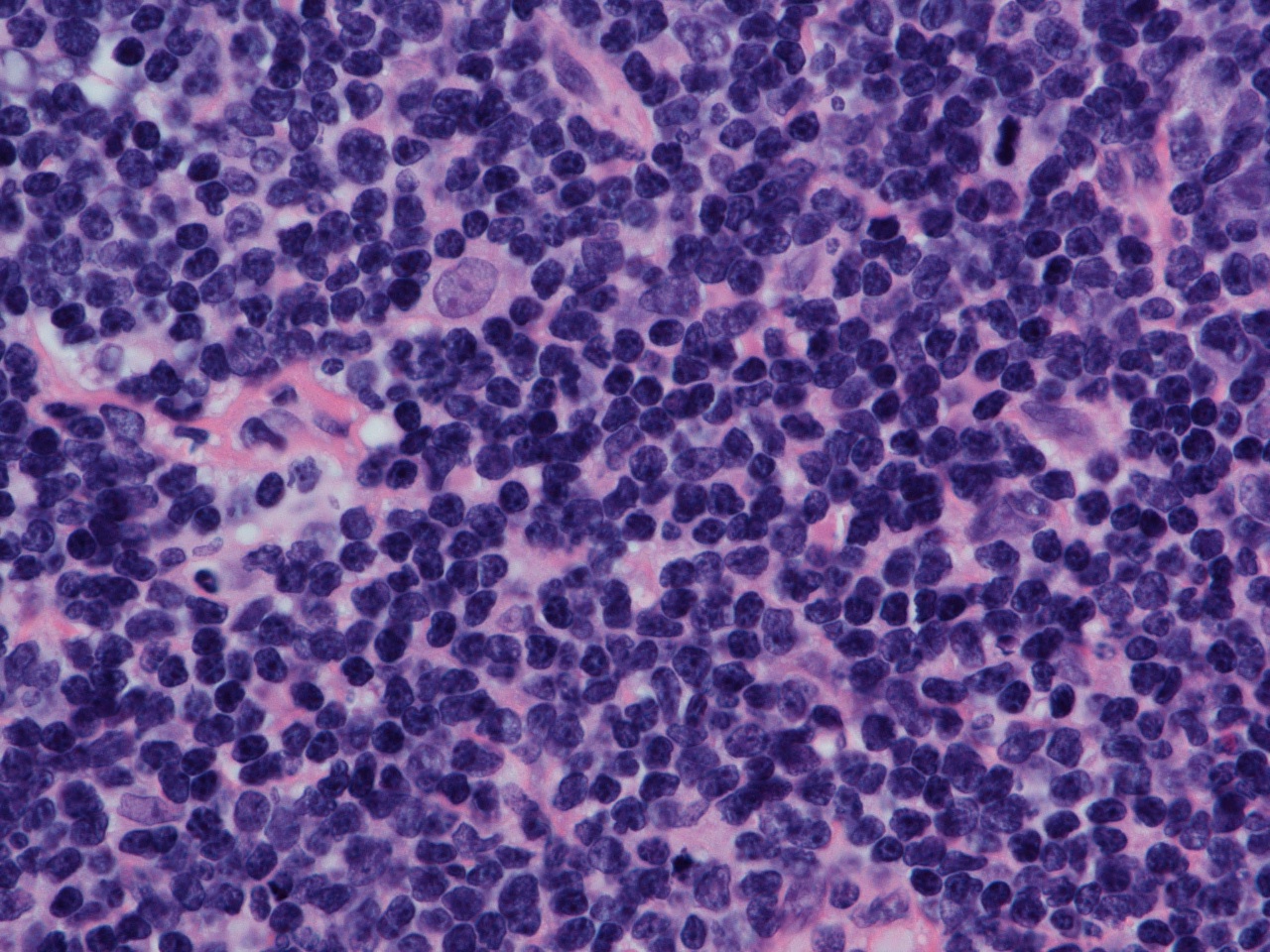 Diagnosis generally requires stained slides of a surgically removed part of a lymph node. Other methods are also commonly used, including cytogenetics and
Diagnosis generally requires stained slides of a surgically removed part of a lymph node. Other methods are also commonly used, including cytogenetics and
non-Hodgkin's lymphoma
Non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL), also known as non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, is a group of hematological malignancy, blood cancers that includes all types of lymphomas except Hodgkin lymphomas. Symptoms include lymphadenopathy, enlarged lymph nodes, fever ...
(NHL), comprising about 6% of NHL cases. There are only about 15,000 patients presently in the United States with mantle cell lymphoma. It is named for the mantle zone
The mantle zone (or just mantle) of a lymphatic nodule (or lymphatic follicle) is an outer ring of small lymphocytes surrounding a germinal center.
It is also known as the "corona".
It contains transient lymphocytes.
It is the location of th ...
of the lymph nodes.
MCL is a subtype of B-cell lymphoma
The B-cell lymphomas are types of lymphoma affecting B cells. Lymphomas are "blood cancers" in the lymph nodes. They develop more frequently in older adults and in immunocompromised individuals.
B-cell lymphomas include both Hodgkin's lympho ...
, due to CD5 positive antigen-naive pregerminal center B-cell within the mantle zone that surrounds normal germinal center
Germinal centers or germinal centres (GCs) are transiently formed structures within B cell zone (follicles) in secondary lymphoid organs – lymph nodes, ileal Peyer's patches, and the spleen – where mature B cells are activated, prolifera ...
follicles. MCL cells generally over-express cyclin D1 due to the t(11:14) translocation, a chromosomal translocation
In genetics, chromosome translocation is a phenomenon that results in unusual rearrangement of chromosomes. This includes balanced and unbalanced translocation, with two main types: reciprocal-, and Robertsonian translocation. Reciprocal translo ...
in the DNA.
Signs and symptoms
At diagnosis, patients typically are in their 60s and present to their physician with advanced disease. About half have B symptoms such asfever
Fever, also referred to as pyrexia, is defined as having a body temperature, temperature above the human body temperature, normal range due to an increase in the body's temperature Human body temperature#Fever, set point. There is not a single ...
, night sweat
Night sweats, also referred to as nocturnal hyperhidrosis (Hyperhidrosis - a medical term for excessive sweating + nocturnal - night), is the repeated occurrence of excessive sweating during sleep. The person may or may not also perspire exces ...
s, or unexplained weight loss
Weight loss, in the context of medicine, health, or physical fitness, refers to a reduction of the total body mass, by a mean loss of fluid, body fat (adipose tissue), or lean mass (namely bone mineral deposits, muscle, tendon, and other conn ...
(over 10% of body weight). Enlarged lymph nodes
Lymphadenopathy or adenopathy is a disease of the lymph nodes, in which they are abnormal in size or consistency. Lymphadenopathy of an inflammatory type (the most common type) is lymphadenitis, producing swollen or enlarged lymph nodes. In cl ...
(for example, a "bump" on the neck, armpits or groin) or enlargement of the spleen are usually present. Bone marrow, liver and gastrointestinal tract involvement occurs relatively early in the course of the disease. Mantle cell lymphoma has been reported in rare cases to be associated with severe allergic reactions to mosquito bites. These reactions involve extensive allergic reactions to mosquito bites which range from greatly enlarged bite sites that may be painful and involve necrosis to systemic symptoms (e.g. fever, swollen lymph nodes, abdominal pain, and diarrhea), or, in extremely rare cases, to life-threatening anaphylaxis. In several of these cases, the mosquito bite allergy (MBA) reaction occurred prior to the diagnosis of MCL suggesting that MBA can be a manifestation of early-developing mantle cell lymphoma.
Pathogenesis
 MCL, like most
MCL, like most cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal b ...
s, results from the acquisition of a combination of (non-inherited) genetic mutations in somatic cells
A somatic cell (from Ancient Greek σῶμα ''sôma'', meaning "body"), or vegetal cell, is any biological cell forming the body of a multicellular organism other than a gamete, germ cell, gametocyte or undifferentiated stem cell. Such cells compo ...
. This leads to a clonal expansion of malignant B lymphocytes. The factors that initiate the genetic alterations are typically not identifiable, and usually occur in people with no particular risk factors for lymphoma development. Because it is an acquired genetic disorder, MCL is neither communicable nor inheritable.
A defining characteristic of MCL is mutation and overexpression of cyclin D1, a cell cycle
The cell cycle, or cell-division cycle, is the series of events that take place in a cell that cause it to divide into two daughter cells. These events include the duplication of its DNA (DNA replication) and some of its organelles, and subs ...
gene, that contributes to the abnormal proliferation of the malignant cells. MCL cells may also be resistant to drug-induced apoptosis
Apoptosis (from grc, ἀπόπτωσις, apóptōsis, 'falling off') is a form of programmed cell death that occurs in multicellular organisms. Biochemical events lead to characteristic cell changes (morphology) and death. These changes incl ...
, making them harder to cure with chemotherapy or radiation. Cells affected by MCL proliferate in a ''nodular'' or ''diffuse'' pattern with two main cytologic variants, ''typical'' or ''blastic''. Typical cases are small to intermediate-sized cells with irregular nuclei. Blastic (aka ''blastoid'') variants have intermediate to large-sized cells with finely dispersed chromatin
Chromatin is a complex of DNA and protein found in eukaryotic cells. The primary function is to package long DNA molecules into more compact, denser structures. This prevents the strands from becoming tangled and also plays important roles in r ...
, and are more aggressive in nature. The tumor cells accumulate in the lymphoid system, including lymph nodes and the spleen, with non-useful cells eventually rendering the system dysfunctional. MCL may also replace normal cells in the bone marrow, which impairs normal blood cell production.
Diagnosis

 Diagnosis generally requires stained slides of a surgically removed part of a lymph node. Other methods are also commonly used, including cytogenetics and
Diagnosis generally requires stained slides of a surgically removed part of a lymph node. Other methods are also commonly used, including cytogenetics and fluorescence in situ hybridization
Fluorescence ''in situ'' hybridization (FISH) is a molecular cytogenetic technique that uses fluorescent probes that bind to only particular parts of a nucleic acid sequence with a high degree of sequence complementarity. It was developed b ...
(FISH). Polymerase chain reaction
The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a method widely used to rapidly make millions to billions of copies (complete or partial) of a specific DNA sample, allowing scientists to take a very small sample of DNA and amplify it (or a part of it) t ...
(PCR) and CER3 clonotypic primers are additional methods, but are less often used.
The immunophenotype Immunophenotyping is a technique used to study the protein expressed by cells. This technique is commonly used in basic science research and laboratory diagnostic purpose. This can be done on tissue section (fresh or fixed tissue), cell suspension ...
profile consists of CD5+ (in about 80% of cases), CD10-/+, and it is usually CD5+ and CD10
Neprilysin (), also known as membrane metallo-endopeptidase (MME), neutral endopeptidase (NEP), cluster of differentiation 10 (CD10), and common acute lymphoblastic leukemia antigen (CALLA) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''MME'' ge ...
-. CD20+, CD23-/+ (though plus in rare cases). Generally, cyclin D1 is expressed. Cyclin D1-negative mantle cell lymphoma can be diagnosed by detecting the SOX11
Transcription factor SOX-11 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''SOX11'' gene.
Function
This intronless gene encodes a member of the group C SOX ( SRY-related HMG-box) transcription factor family involved in the regulation of embryo ...
marker. The workup for mantle cell lymphoma is similar to the workup for many indolent lymphomas and certain aggressive lymphomas.
Mantle cell lymphoma is a systemic disease with frequent involvement of the bone marrow and gastrointestinal tract (generally showing polyposis in the lining). There is also a not-uncommon leukemic phase, marked by its presence in the blood. For this reason, both the peripheral blood and bone marrow are evaluated for the presence of malignant cells. Chest, abdominal, and pelvic CT scans are routinely performed.
Since mantle cell lymphoma may present a lymphomatous polyposis coli and colon involvement is common, colonoscopy is considered a routine part of the evaluation. Upper endoscopy and neck CT scan may be helpful in selected cases. In some patients with the blastic variant, lumbar puncture is done to evaluate the spinal fluid for involvement.
CT scan
PET scan
Positron emission tomography (PET) is a functional imaging technique that uses radioactive substances known as radiotracers to visualize and measure changes in metabolic processes, and in other physiological activities including blood flow, r ...
Treatments
There are no proven standards of treatment for MCL, and there is no consensus among specialists on how to treat it optimally. Many regimens are available and often get good response rates, but patients almost always get disease progression after chemotherapy. Each relapse is typically more difficult to treat, and relapse is generally faster. Regimens are available that treat relapses, and new approaches are under test. Because of the aforementioned factors, many MCL patients enroll in clinical trials to get the latest treatments. There are four classes of treatments in general use:chemotherapy
Chemotherapy (often abbreviated to chemo and sometimes CTX or CTx) is a type of cancer treatment that uses one or more anti-cancer drugs (chemotherapeutic agents or alkylating agents) as part of a standardized chemotherapy regimen. Chemotherap ...
, immunotherapy
Immunotherapy or biological therapy is the treatment of disease by activating or suppressing the immune system. Immunotherapies designed to elicit or amplify an immune response are classified as ''activation immunotherapies,'' while immunotherap ...
, radioimmunotherapy
Radioimmunotherapy (RIT) uses an antibody labeled with a radionuclide to deliver cytotoxic radiation to a target cell. It is a form of unsealed source radiotherapy. In cancer therapy, an antibody with specificity for a tumor-associated antigen i ...
and biologic agents. The phases of treatment are generally: frontline, following diagnosis, consolidation, after frontline response (to prolong remissions), and relapse. Relapse is usually experienced multiple times.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy (often abbreviated to chemo and sometimes CTX or CTx) is a type of cancer treatment that uses one or more anti-cancer drugs (chemotherapeutic agents or alkylating agents) as part of a standardized chemotherapy regimen. Chemotherap ...
is widely used as frontline treatment, and often is not repeated in relapse due to side effects. Alternate chemotherapy is sometimes used at first relapse. For frontline treatment, CHOP with rituximab
Rituximab, sold under the brand name Rituxan among others, is a monoclonal antibody medication used to treat certain autoimmune diseases and types of cancer. It is used for non-Hodgkin lymphoma, chronic lymphocytic leukemia (in non-geriatric pa ...
is the most common chemotherapy, and often given as outpatient by IV. A stronger chemotherapy with greater side effects (mostly hematologic) is HyperCVAD Hyper-CVAD is a chemotherapy regimen used to treat some forms of leukemia, high-grade non-Hodgkin lymphoma, and lymphoblastic leukemia.
Summary
Hyper-CVAD chemotherapy consists of two combinations of drugs (courses A and B) given in an alternatin ...
, often given in the hospital setting, with rituximab and generally to fitter patients (some of which are over 65). HyperCVAD is becoming popular and showing promising results, especially with rituximab. It can be used on some elderly (over 65) patients, but seems only beneficial when the baseline Beta-2-MG blood test was normal. It is showing better complete remissions (CR) and progression-free survival (PFS) than CHOP regimens. A less intensive option is bendamustine
Bendamustine, sold under the brand name Treanda among others, is a chemotherapy medication used in the treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), multiple myeloma, and non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. It is given by injection into a vein.
Common s ...
with rituximab.
Second line treatment may include fludarabine
Fludarabine is a purine analogue and antineoplastic agent. It is generally used as its 5-O-phosphorylated form known as fludarabine phosphate,
sold under the brand name Fludara among others. It is a chemotherapy medication used in the treatmen ...
, combined with cyclophosphamide
Cyclophosphamide (CP), also known as cytophosphane among other names, is a medication used as chemotherapy and to suppress the immune system. As chemotherapy it is used to treat lymphoma, multiple myeloma, leukemia, ovarian cancer, breast cancer ...
and/or mitoxantrone, usually with rituximab. Cladribine
Cladribine, sold under the brand name Leustatin, among others, is a medication used to treat hairy cell leukemia (leukemic reticuloendotheliosis) and B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia.
Cladribine, sold under the brand name Mavenclad, is indicat ...
and clofarabine
Clofarabine is a purine nucleoside antimetabolite marketed in the United States and Canada as Clolar. In Europe and Australia/New Zealand the product is marketed under the name Evoltra. It is FDA-approved for treating relapsed or refractory acute ...
are two other medications being investigated in MCL. A relatively new regimen that uses old medications is PEP-C, which includes relatively small, daily doses of prednisone
Prednisone is a glucocorticoid medication mostly used to immunosuppressive drug, suppress the immune system and decrease inflammation in conditions such as asthma, COPD, and rheumatologic diseases. It is also used to treat high blood calcium ...
, etoposide
Etoposide, sold under the brand name Vepesid among others, is a chemotherapy medication used for the treatments of a number of types of cancer including testicular cancer, lung cancer, lymphoma, leukemia, neuroblastoma, and ovarian cancer. It is ...
, procarbazine
Procarbazine is a chemotherapy medication used for the treatment of Hodgkin's lymphoma and brain cancers. For Hodgkin's it is often used together with chlormethine, vincristine, and prednisone while for brain cancers such as glioblastoma multif ...
, and cyclophosphamide, taken orally, has proven effective for relapsed patients. According to Dr. John Leonard, PEP-C may have anti-angiogenetic properties, something that he and his colleagues are testing through an ongoing drug trial.
Another approach involves using very high doses of chemotherapy, sometimes combined with total body irradiation (TBI), in an attempt to destroy all evidence of the disease. The downside to this is the destruction of the patient's entire immune system as well, requiring rescue by transplantation of a new immune system (hematopoietic stem cell transplantation
Hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation (HSCT) is the transplantation of multipotent hematopoietic stem cells, usually derived from bone marrow, peripheral blood, or umbilical cord blood in order to replicate inside of a patient and to produce ...
), using either autologous stem cell transplantation
Autologous stem-cell transplantation (also called autogenous, autogeneic, or autogenic stem-cell transplantation and abbreviated auto-SCT) is autologous transplantation of stem cells—that is, transplantation in which stem cells ( undifferentiat ...
, or those from a matched donor (an allogeneic stem cell transplant). A presentation at the December 2007 American Society of Hematology (ASH) conference by Christian Geisler, chairman of the Nordic Lymphoma Group claimed that according to trial results, mantle cell lymphoma is potentially curable with very intensive chemo-immunotherapy followed by a stem cell transplant, when treated upon first presentation of the disease.
These results seem to be confirmed by a large trial of the European Mantle Cell Lymphoma Network indicating that induction regimens containing monoclonal antibodies and high dose ARA-C (Cytarabine) followed by ASCT should become the new standard of care of MCL patients up to approximately 65 years.
A study released in April 2013 showed that patients with previously untreated indolent lymphoma, bendamustine plus rituximab can be considered as a preferred first-line treatment approach to R-CHOP because of increased progression-free survival and fewer toxic effects.
Immunotherapy
Immune-based therapy is dominated by the use of therituximab
Rituximab, sold under the brand name Rituxan among others, is a monoclonal antibody medication used to treat certain autoimmune diseases and types of cancer. It is used for non-Hodgkin lymphoma, chronic lymphocytic leukemia (in non-geriatric pa ...
monoclonal antibody, sold under the trade name Rituxan (or as Mabthera in Europe and Australia). Rituximab may have good activity against MCL as a single agent, but it is typically given in combination with chemotherapies, which prolongs response duration. There are newer variations on monoclonal antibodies
A monoclonal antibody (mAb, more rarely called moAb) is an antibody produced from a cell Lineage made by cloning a unique white blood cell. All subsequent antibodies derived this way trace back to a unique parent cell.
Monoclonal antibodies ca ...
combined with radioactive molecules known as radioimmunotherapy
Radioimmunotherapy (RIT) uses an antibody labeled with a radionuclide to deliver cytotoxic radiation to a target cell. It is a form of unsealed source radiotherapy. In cancer therapy, an antibody with specificity for a tumor-associated antigen i ...
(RIT). These include Zevalin
Ibritumomab tiuxetan (pronounced ), sold under the trade name Zevalin, is a monoclonal antibody radioimmunotherapy treatment for non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. The drug uses the monoclonal mouse IgG1 antibody ibritumomab in conjunction with the chelator ...
and Bexxar
Tositumomab is a murine monoclonal antibody which targets the CD20 antigen produced in mammalian cell. It was combined with iodine-131 to produce a radiopharmaceutical for unsealed source radiotherapy, Iodine-131 Tositumomab (branded as Bexxar), fo ...
. Rituximab has also been used in small numbers of patients in combination with thalidomide
Thalidomide, sold under the brand names Contergan and Thalomid among others, is a medication used to treat a number of cancers (including multiple myeloma), graft-versus-host disease, and a number of skin conditions including complications of ...
with some effect. In contrast to these antibody-based 'passive' immunotherapies, the field of 'active' immunotherapy tries to activate a patient's immune system to specifically eliminate their own tumor cells. Examples of active immunotherapy include cancer vaccines, adoptive cell transfer
Adoptive cell transfer (ACT) is the transfer of cells into a patient. The cells may have originated from the patient or from another individual. The cells are most commonly derived from the immune system with the goal of improving immune functiona ...
, and immunotransplant, which combines vaccination and autologous stem cell transplant
Autologous stem-cell transplantation (also called autogenous, autogeneic, or autogenic stem-cell transplantation and abbreviated auto-SCT) is autotransplantation, autologous transplantation of stem cells—that is, transplantation in which stem cel ...
. Though no active immunotherapies are currently a standard of care, numerous clinical trial
Clinical trials are prospective biomedical or behavioral research studies on human participants designed to answer specific questions about biomedical or behavioral interventions, including new treatments (such as novel vaccines, drugs, dietar ...
s are ongoing.
Targeted therapy
Two Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitors (BTKi), one In November 2013,ibrutinib
Ibrutinib, sold under the brand name Imbruvica among others, is a small molecule drug that inhibits B-cell proliferation and survival by irreversibly binding the protein Bruton's tyrosine kinase (BTK). Blocking BTK inhibits the B-cell receptor ...
(trade name Imbruvica, Pharmacyclics LLC) and in October 2017, acalabrutinib
Acalabrutinib, sold under the brand name Calquence, is a medication used to treat various types of non-Hodgkin lymphoma, including mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) and chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic leukemia (CLL/SLL). It may be used ...
(trade name Calquence, AstraZeneca Pharmaceuticals LP) were approved in the United States for treating MCL.
Other targeted agents include the proteasome inhibitor bortezomib
Bortezomib, sold under the brand name Velcade among others, is an anti-cancer medication used to treat multiple myeloma and mantle cell lymphoma. This includes multiple myeloma in those who have and have not previously received treatment. It is ...
, mTOR
The mammalian target of sirolimus, rapamycin (mTOR), also referred to as the mechanistic target of rapamycin, and sometimes called FK506-binding protein 12-rapamycin-associated protein 1 (FRAP1), is a kinase that in humans is encoded by the ''MT ...
inhibitors such as temsirolimus
Temsirolimus, sold under the brand name Torisel, is an intravenous drug for the treatment of renal cell carcinoma (RCC), developed by Wyeth Pharmaceuticals and approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in May 2007, and was also appro ...
, and the P110δ
Phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase catalytic subunit delta isoform also known as phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) delta isoform or p110δ is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''PIK3CD'' gene.
p110δ regulates immune function. ...
inhibitor GS-1101.
In November 2019, zanubrutinib
Zanubrutinib, sold under the brand name Brukinsa, is a medication used for the treatment of mantle cell lymphoma (MCL), Waldenström's macroglobulinemia (WM), marginal zone lymphoma (MZL), and chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). Zanubrutinib ...
(Brukinsa) was approved in the United States with an indication for the treatment of adults with mantle cell lymphoma who have received at least one prior therapy.
Gene therapy
Brexucabtagene autoleucel (Tecartus) was approved for medical use in the United States in July 2020, with an indication for the treatment of adults with relapsed or refractory mantle cell lymphoma. It was approved for medical use in the European Union in December 2020. Each dose of brexucabtagene autoleucel is a customized treatment created using the recipient's own immune system to help fight the lymphoma. The recipient'sT cell
A T cell is a type of lymphocyte. T cells are one of the important white blood cells of the immune system and play a central role in the adaptive immune response. T cells can be distinguished from other lymphocytes by the presence of a T-cell r ...
s, a type of white blood cell, are collected and genetically modified to include a new gene that facilitates the targeting and killing of the lymphoma cells. These modified T cells are then infused back into the recipient.
Prognosis
Recent clinical advances in mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) have seen standard‐of‐care treatment algorithms transformed. Frontline rituximab combination therapy, high dose cytarabine‐based induction in younger patients and, more recently, Bruton Tyrosine Kinase (BTK) inhibitors in the relapse setting have all demonstrated survival advantage in clinical trials (Wang et al., 2013; Eskelund et al., 2016; Rule et al., 2016). Over the last 15 years these practices have gradually become embedded in clinical practice and real‐world data has observed corresponding improvements in patient survival (Abrahamsson et al., 2014; Leux et al., 2014). The overall 5-year survival rate for MCL is generally 50% (advanced stage MCL) to 70% (for limited-stage MCL). Prognosis for individuals with MCL is problematic and indexes do not work as well due to patients presenting with advanced stage disease. Staging is used but is not very informative, since the malignant B-cells can travel freely though the lymphatic system and therefore most patients are at stage III or IV at diagnosis. Prognosis is not strongly affected by staging in MCL and the concept of metastasis does not really apply. The Mantle Cell Lymphoma International Prognostic Index (MIPI) was derived from a data set of 455 advanced stage MCL patients treated in series of clinical trials in Germany/Europe. Of the evaluable population, approximately 18% were treated with high-dose therapy and stem cell transplantation in first remission. The MIPI is able to classify patients into three risk groups: low risk (median survival not reached after median 32 months follow-up and 5-year OS rate of 60%), intermediate risk (median survival 51 months) and high risk (median survival 29 months). In addition to the 4 independent prognostic factors included in the model, the cell proliferation index (Ki-67) was also shown to have additional prognostic relevance. When the Ki67 is available, a biologic MIPI can be calculated. MCL is one of the few NHLs that can cross the boundary into the brain, yet it can be treated in that event. There are a number of prognostic indicators that have been studied. There is not universal agreement on their importance or usefulness in prognosis. Ki-67 is an indicator of how fast cells mature and is expressed in a range from about 10% to 90%. The lower the percentage, the lower the speed of maturity, and the more indolent the disease. Katzenberger et al. Blood 2006;107:3407 graphs survival versus time for subsets of patients with varying Ki-67 indices. He shows median survival times of about one year for 61-90% Ki-67 and nearly 4 years for 5-20% Ki-67 index. MCL cell types can aid in prognosis in a subjective way. Blastic is a larger cell type. Diffuse is spread through the node. Nodular are small groups of collected cells spread through the node. Diffuse and nodular are similar in behavior. Blastic is faster growing and it is harder to get long remissions. Some thought is that given a long time, some non-blastic MCL transforms to blastic. Although survival of most blastic patients is shorter, some data shows that 25% of blastic MCL patients survive to 5 years. That is longer than diffuse type and almost as long as nodular (almost 7 yrs).Beta-2 microglobulin
β2 microglobulin (B2M) is a component of MHC class I molecules. MHC class I molecules have α1, α2, and α3 proteins which are present on all nucleated cells (excluding red blood cells). In humans, the β2 microglobulin protein is encoded by th ...
is another risk factor in MCL used primarily for transplant patients. Values less than three have yielded 95% overall survival to six years for auto SCT where over three yields a median of 44 most overall survival for auto SCT (Khouri 03). This is not yet fully validated.
Testing for high levels of Lactate dehydrogenase
Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH or LD) is an enzyme found in nearly all living cells. LDH catalyzes the conversion of lactate to pyruvate and back, as it converts NAD+ to NADH and back. A dehydrogenase is an enzyme that transfers a hydride from on ...
(LDH) in NHL patients is useful because LDH is released when body tissues break down for ''any'' reason. While it cannot be used as a sole means of diagnosing NHL, it is a surrogate for tracking tumor burden in those diagnosed by other means. The normal range is approximately 100–190.
Epidemiology
6% ofnon-Hodgkin lymphoma
Non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL), also known as non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, is a group of blood cancers that includes all types of lymphomas except Hodgkin lymphomas. Symptoms include enlarged lymph nodes, fever, night sweats, weight loss, and tiredness. ...
cases are mantle cell lymphoma. , the ratio of males to females affected is about 4:1.
See also
* ''In situ'' mantle cell lymphoma *List of hematologic conditions
:''This is an incomplete list, which may never be able to satisfy certain standards for completion.''
There are many conditions of or affecting the human hematologic system—the biological system that includes plasma, platelets, leukocytes, an ...
References
Further reading
* * *External links
{{Portal bar , Medicine Non-Hodgkin lymphoma